1. Business Process Framework (BPF)
The software modules that form the essential elements of the Business Process Framework (i.e. the system's feeder and control processes) are illustrated by squares and workflow bars respectively (see diagram one). Click 'FPD10 Investment Portfolio' to explore a second feeder process example.
Formatted dataflows (see SDI below) are used within the control processes to maintain the status of workflows across four subsystems (demand, transformation, service and value) and allow feeder process activity to be both audited and authorised.
2. Information Architecture (IA)
Content Strategy is configured using a catalogue of narratives and structure diagrams which may be implemented as standard or adapted to suit specific enterprise requirements. However, content processes developed in-house must interface with the standard code that seamlessly captures relevant event metrics (such as business improvement requested, unit test audit complete or say, service failure).
Display transformation workflow and explore further feeder system examples FPT07,and FPT08 (compliance and security engineering respectively). Re-display transformation workflow and click bar 'TRANSFORMATION' to explore the Transformation Metrics ' (RHS). Conclude this part of module 2 by exploring Feeder Process 'FPS06 Performance Engineering' along with the subsystem Control Process for Service Delivery and 'FPV03 Financial Plan' with the subsystem Control Process for Value Measurement.
User Experience (UX) is designed to enhance usability, accessibility and the fulfilment given by the interaction between the ADT user and content. Practical consideration of multimedia and certain communication styles, such as analytical, intuitive, functional and personal will play a part in the aesthetic appeal of this feature.
3. Standard Data Interface (SDI)
This model uses approximately 120 unique dataflows, classified by subsystem, to seamlessly capture IT process event metrics. Note that the system excludes the capture of personal behaviour data and has no impact on an employee's personal assessment; this function remains a separate managerial responsibility. Each dataflowmouse
BUSINESS IMPROVEMENT REQUEST (flow 101005)
DTD
<!ELEMENT busVar (projectId, devStrategy, reqType)>
<!ELEMENT projectId (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT devStrategy (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT reqType (#PCDATA)>
SCHEMA
<xs:element name="busVar">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="projectId" type="xs:projectId"/>
<xs:element name="devStrategy" type="xs:strategy"/ >
<xs:element name="reqType" type="xs:requesttype"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
XML
<busVar>
<projectId>01-0000598</projectId>
<devType>Structured </devStrategy>
<reqType>Internal </reqType>
</busVar>
is verified by a standard data schema (say XSD) allowing transmission via the standard interface to the Database, Authorisation and Reporting subsystems. As mentioned in module 1, users deploying an external solution must configure the required data before actioning a dataflow transmission and update request.
4. Real Time Reporting (RTR)
The IT Information database is a repository for IT activity over time and supports standard, parameter driven reports (say using periods, types, targets and so on). For example The Conversion Rate Reportmouse 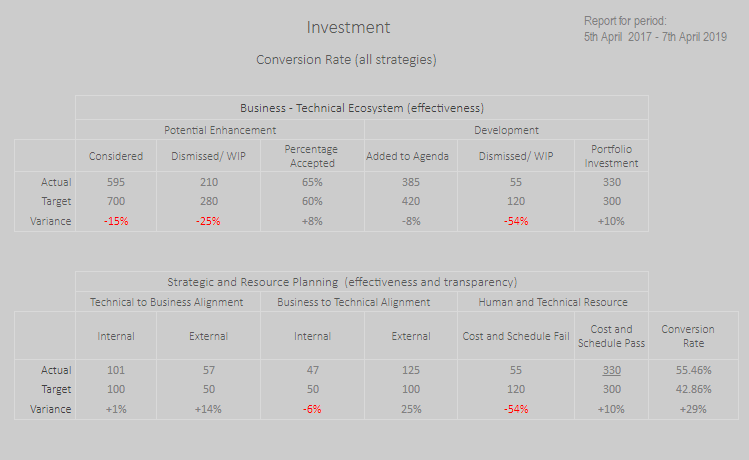 and The Investment Progress Reportmouse
and The Investment Progress Reportmouse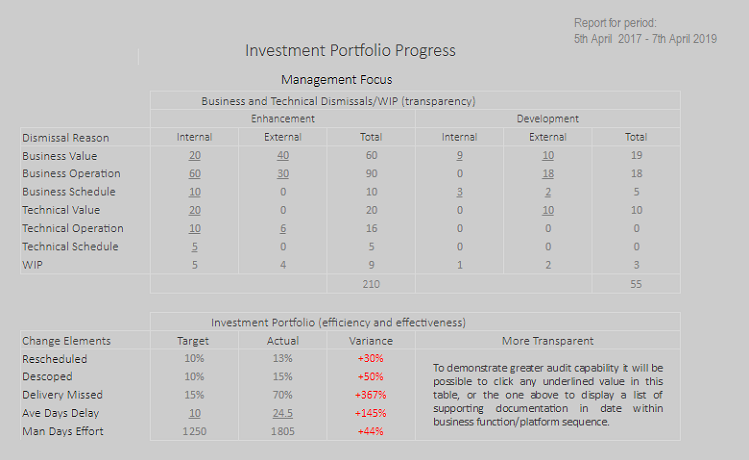 which give an indication of an installation's drive for competitive advantage and the level of attention paid to ineffective requests respectively. A Report Generator extends statistical analysis capability by offering custom defined reports. All the information provided by the reporting facility reflects the actual time during which processes or events occur.
which give an indication of an installation's drive for competitive advantage and the level of attention paid to ineffective requests respectively. A Report Generator extends statistical analysis capability by offering custom defined reports. All the information provided by the reporting facility reflects the actual time during which processes or events occur.